Guidelines for pH Electrode Maintenance and Use
Like any piece of equipment pH electrodes have a certain life expectancy. However, with proper care and maintainence you can maximize your electrode life.
Knowing factors that influence electrode life can help you better understand and care for your electrode.
Learn MoreExtend the life of your pH electrode by following the steps below.
1. Hydration of the glass bulb
A very thin layer of water forms on the pH glass sensor. This layer is known as the hydrated layer. As an electrochemical sensor the hydration layer affects the voltage generated by the pH sensor.
A probe that has a hydrated layer will generate a different voltage in a pH buffer than a pH electrode without a hydrated layer. So calibrating a dry electrode will cause inaccurate readings when taking measurements as the hydration layer is formed. A dry probe needs to be hydrated by placing in storage solution before calibration. The hydrated layer takes 3-4 hours to form.
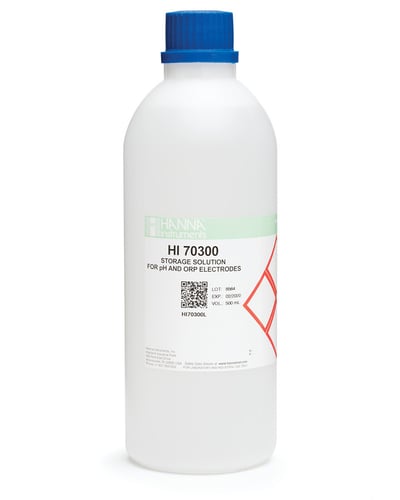

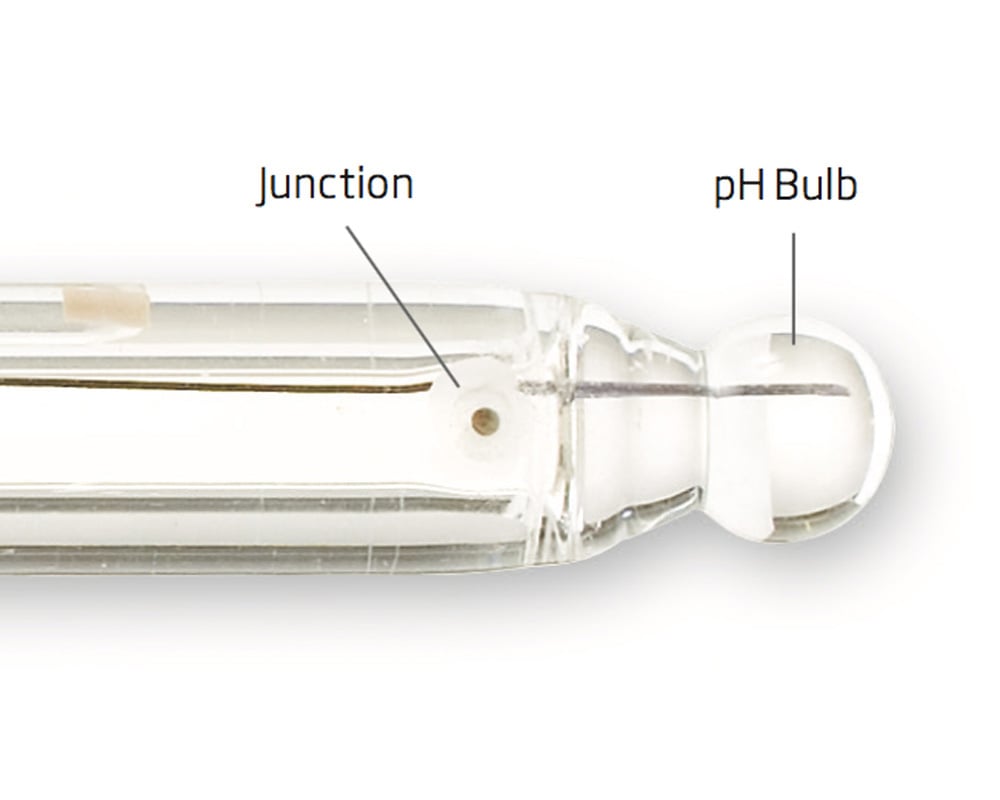
2. Hydration of the junction
Every combination pH electrode has a junction. A junction is a barrier between the internal reference wire and the sample that is measured. The reference cell has a salt solution that leaks through the junction as part of the electrical circuit. If a probe is dry the salt will precipitate in the junction causing to be clogged. The pH readings will be erratic. A dry probe needs to have the junction hydrated to work properly.
- Specially formulated to keep the glass hydrated while minimizing organic growth
- Keeps junction hydrated for fast response
- Available in 230 and 500 ml bottles

3. Fill Solution Level for Refillable pH Electrodes
pH electrodes that are refillable need to have their electrolyte (salt) level checked. The probe should be filled when the level falls below ½” from the fill hole opening. Having enough fill solution ensures that the reference wire is in solution for a single junction electrode and continuity with the inner junction for a double junction electrode. A proper level also allows for adequate head pressure to force electrolyte through the junction.

4. Remove/Loosen Reference Fill Cap When in Use
- In order to create head pressure the fill cap must be loosened or removed from the top of the electrode. Removing/loosening the reference fill cap allows for air to enter into the reference cell. The solution within the probe will want to flow through the junction resulting in increased stability when taking a reading.
- Fill solutions for both single and double junction electrodes
- Single junction electrodes use 3.5 M KCl with silver chloride
- Double junction electrodes use 3.5 M KCl
- Available in a variety of sizes
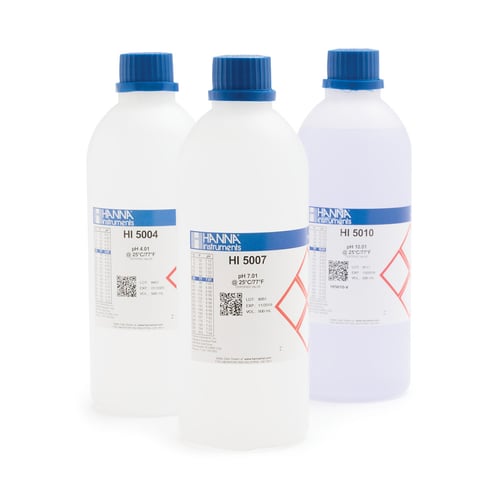

5. Calibration Buffers
Fresh calibration solution should be used when calibrating a pH electrode. All pH measurements are based on the pH calibration solution as a reference point.
The pH calibration buffer is a water-based solution that will change over time. This is especially true for pH 10.01 buffer that will actually decrease in pH as atmospheric carbon dioxide enters the solution.
Bottles of buffer should be replaced after they have been opened for 6 months.
Never pour calibration buffer back into the bottle.
- Basic, Technical, and Millesimal pH buffers
- Accurate to ±0.01 pH for Basic and Technical
- Accurate to ±0.002 pH for Millesimal
- Technical and Millesimal buffers supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (COA)
6. Calibration of the pH Electrode
The pH electrode should be rinsed in purified water (RO, DI, or distilled) before placing in any pH calibration buffer. This will reduce the chance of contaminating the buffer.
A best practice would be to use two beakers/containers for each calibration buffer. The process would be to rinse the pH electrode with purified water then rinse the probe in one of the beakers with the buffer then place the probe in the second beaker with buffer.
This procedure would be repeated for multiple calibration points.
For two point calibration the pH buffers used should bracket the expected pH reading. For example I expect a pH 5 reading then the pH electrode should be calibrated in pH 7 and pH 4 buffers.
- Hanna offers pH buffers from pH 1.000 to 13.00
- Available in a variety of sizes
- Available in variety of packaging from single use packets to 1 gallon bottles
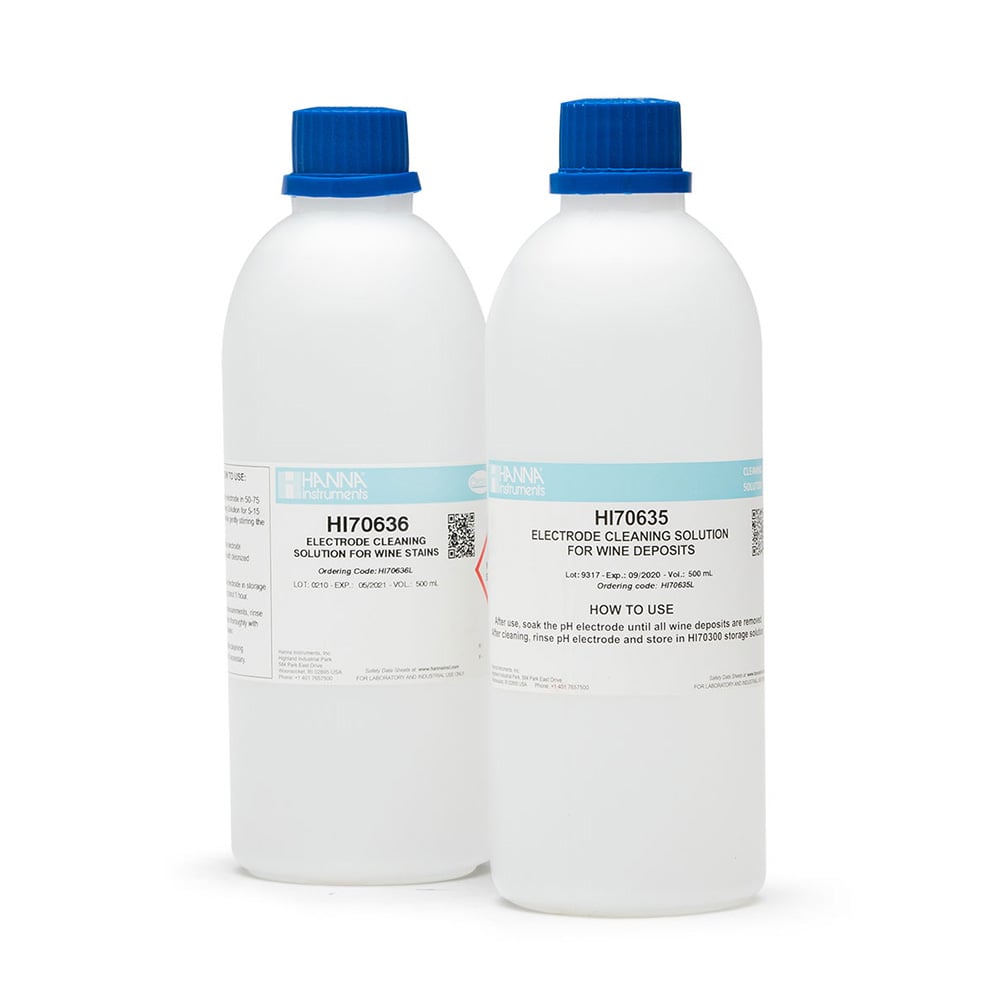

7. Cleaning a pH Electrode
The pH electrode should be cleaned periodically. A coating will form on the glass bulb that will cause errors in measurements and drifting/erratic readings. A typical cleaning procedure is to place the electrode in a cleaning solution for 15 minutes. After that the probe is rinsed with purified water and then placed in storage solution for at least 2-3 hours before using. It is important to note that there are many different types of cleaning solutions available based on the application. Solutions include ones for proteins, inorganics, food and wine stains to name just a few.
- Selection of cleaning solutions from general purpose to those specific for your applications
- Available in 500 ml bottles or single-use sachets
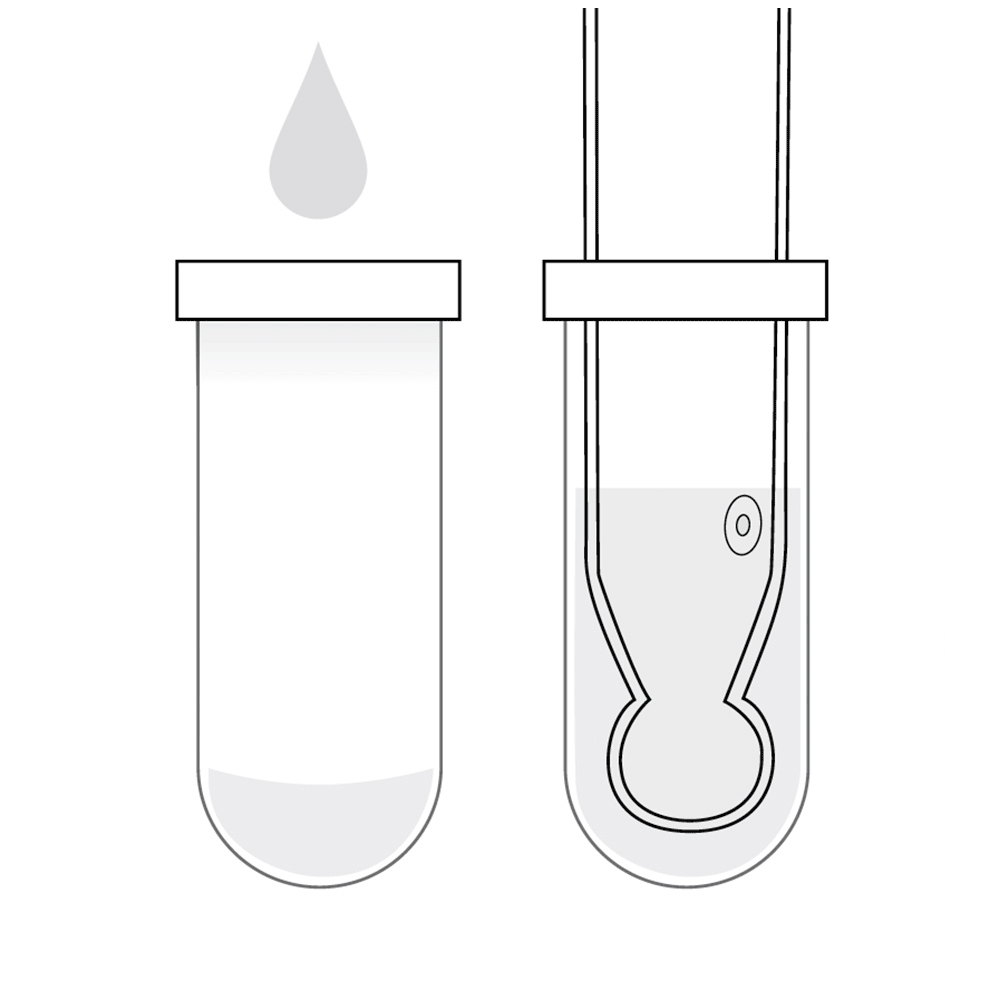
8. Storage of the pH electrode
The pH electrode bulb and junction needs to be kept hydrated.
With benchtop meters a small amount of storage solution is placed in a beaker. With the probe lowered into the beaker the junction should be covered.
For portable meters a small amount of storage solution is placed in the protective cap and the cap placed on the probe.
NEVER STORE THE pH ELECTRODE IN PURIFIED WATER
- Storing the pH electrode in purified water (RO, DI, or distilled) will shorten the life of your pH electrode.
- The reference cell has a high salt solution. Placing the probe in purified water will cause the salt to diffuse out and the water to go in. Storage solution is not only formulated to maintain the reference salt concentration but also has chemicals to keep bacteria and fungus from growing in the solution. If storage solution is not available then use pH 4 buffer.
9. Tips
- Salt crystals around the fill cap of a refillable pH electrode or by the protective cap placed over the bulb are normal to see. Just rinse with water to remove the salt build up.
- Any air bubbles in the pH bulb or by the junction need to be removed. Gently shake the pH electrode like a spirit filled thermometer to displace the air bubble.
- Never wipe the pH electrode with a cloth or any other type of material. Any static formed will harm the electrode.
- Do not expose to high temperatures (>150 °F/65 °C) unless the probe is designed for it.
- Always rinse the probe with purified water to clean of contaminants before, during and after use.
- Calibrate frequently. Some guidelines to follow:
- Periodic user (1-2 times per month) – calibrate the day of use
- Weekly user (1-2 times per week) – calibrate the day of use
- Daily user (1-2 times per day) – calibrate the day of use
- Daily user (>2 times per day) – calibrate every 4-6 hours